[HCI] 2. Human 1
the human
- Information I/O …
- visual, auditory, haptic, movement
- Information stored in memory
- sensory, short-term, long-term
- Information processed and applied
- reasoning, problem solving, skill, error
- Emotion influences human capabilities
- Each person is different
Vision
- Two stages in vision
- Physical reception of stimulus (입력을 받아들이는 감각)
- Eyes
- Ears
- Fingers
- Processing and interpretation of stimulus (카메라로 사진을 찍고 나서의 처리과정과 같은 과정)
- Perception
- Memory
- Physical reception of stimulus (입력을 받아들이는 감각)
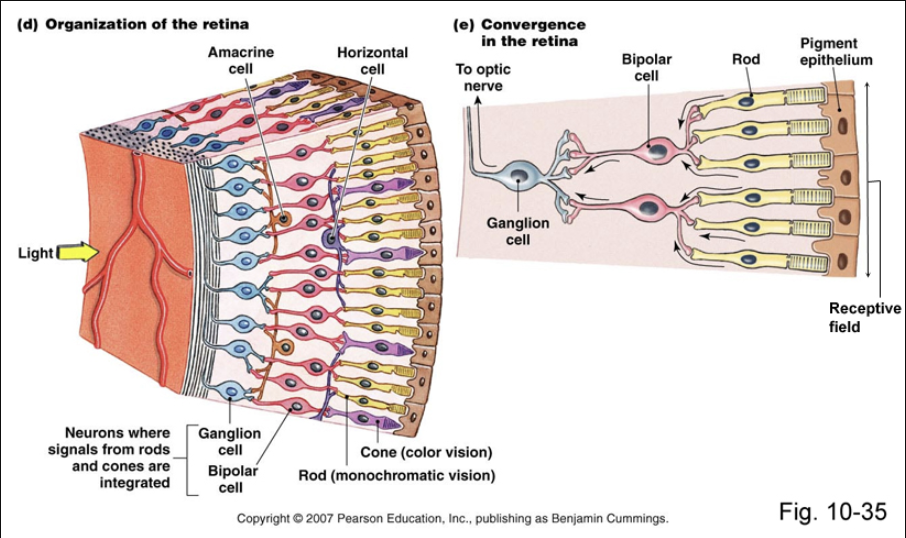
The Eye - physical reception
- Mechanism for receiving light and transforming it into electrical energy
- Light reflects from objects
- Images are focused upside-down on retina
- Retina contains rods(모든 종류의 파장이 가능해서 강조를 파악) for low light vision and cones(특정 주파수를 통해 wavelength에 의해서 가능한 cell) for colour vision
- Ganglion cells (brain!) detect pattern and movement
Interpreting the signal
- Size and depth
- Visual angle indicates how much of view object occupies (relates to size and distance from eye)
- Visual acuity is ability to perceive detail (limited)
- Familiar objects perceived as constant size (in spite of changes in visual angle when far away)
- 책상을 예로 우리의 시각에서는 사다리꼴처럼 보이지만 뇌에서는 이를 직사각형으로 인식하거나 아무리 멀리 있어도 그 크기를 가늠할 수 있는 것이다.
- Cues like overlapping help perception of size and depth
Interpreting the signal (cont)
- Brightness
- Subjective reaction to levels of light
- Affected by luminance of object
- Measured by just noticeable difference
- Visual acuity increases with luminance as does flicker(깜빡깜빡)
- Color
- Made up of hue, intensity, saturation
- Cones sensitive to colour wavelengths
- Blue acuity is lowest (파란색의 명암이 구분이 제일 힘듬; 그린 > 레드 > 블루)
- acuity: 명확히 보고 듣고 생각하는 능력
- 8% males and 1% females colour blind
- The visual system compensates for:
- Movement
- Changes in luminance.
- Context is used to resolve ambiguity
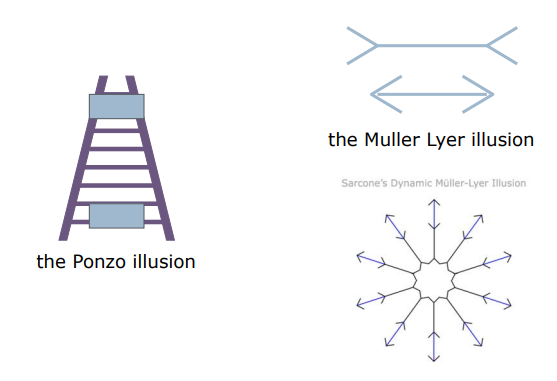
- Optical illusions(왜곡) sometimes occur due to overcompensation
Optical Illusions
Reading
- Several stages:
- Visual pattern perceived
- Decoded using internal representation of language
- Interpreted using knowledge of syntax(문법), semantics(의미), pragmatics(맥락)
- Reading involves saccades(홱 스킵하면서 읽는) and fixations(가만히 있는)
- Perception occurs during fixations
- Word shape is important to recognition
- Negative contrast improves reading from computer screen
Hearing
- Provides information about environment: distances, directions, objects etc.
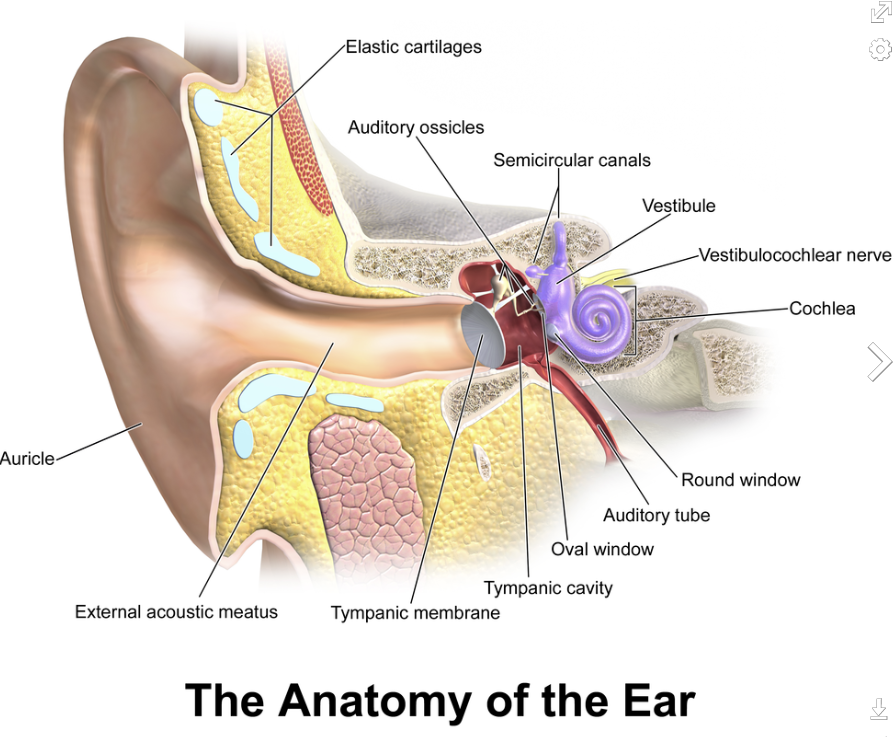
- Physical apparatus:
- Outer ear: protects inner and amplifies sound
- Middle ear: transmits sound waves as vibrations to inner ear
- Inner ear: chemical transmitters are released and cause impulses in auditory nerve
- Sound
- Pitch: sound frequency (높낮이)
- Loudness: amplitude (크기)
- Timbre: type or quality (음색)
- Humans can hear frequencies from 20Hz to 15kHz
- Less accurate distinguishing high frequencies than low.
- Auditory system filters sounds
- Can attend to sounds over background noise.
- For example, the cocktail party phenomenon(웅성웅성하고 시끄러운 상황에서 대화를 하고 있는 상대의 말소리만 catch하는 능력).
Touch
- Provides important feedback about environment.
- May be key sense for someone who is visually impaired.
- Stimulus received via receptors in the skin:
- Thermoreceptors: heat and cold
- Nociceptors: pain
- Mechanoreceptors: pressure (some instant, some continuous)
- Some areas more sensitive than others e.g. fingers.
- Kinesthesis - awareness of body position
- 눈을 감고도 내가 어떤 자세를 취하고 있는지를 인식하고 있는 것.
- Affects comfort and performance.
Movement
- Time taken to respond to stimulus:
- reaction time + movement time
- Movement time dependent on age, fitness etc.
- Reaction time - dependent on stimulus type:
- visual ~ 200ms
- auditory ~ 150 ms
- pain ~ 700ms
- Increasing reaction time decreases accuracy in the unskilled operator but not in the skilled operator.
Movement (cont)
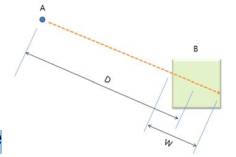
- Fitts’ Law describes the time taken to hit a screen target
- Shannon formulation (Dr. Scott MacKenzie)

- where:
- a and b are empirically determined constants
- Mt is movement time
- D is Distance
- W is Width of target
targets as large as possible distances as small as possible
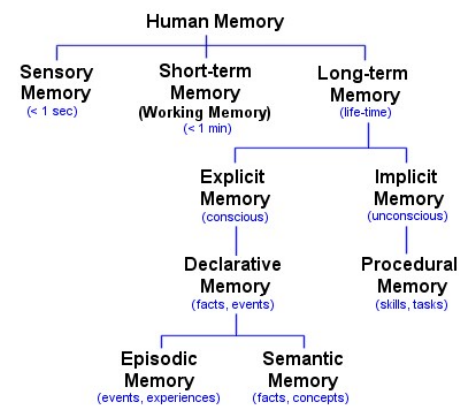
Memory
- There are three types of memory function:

- Selection of stimuli governed by level of arousal.
Sensory Memory
- Buffers for stimuli received through senses
- Iconic memory: visual stimuli
- Echoic memory: aural stimuli
- Haptic memory: tactile stimuli
- Examples
- Sparkler trail
- Someone else’s name called in public
- Continuously overwritten

Short-term Memory (STM)
- Scratch-pad for temporary recall
- Rapid access ~ 70ms
- Rapid decay ~ 20s to 30s
- Limited capacity – 7 ± 2 chunks
Examples
212348278493202
0121 414 2626
HEC ATR ANU PTH ETR EET
Long-term Memory (LTM)
- Repository for all our knowledge
- Slow access ~ 1 to 10 seconds
- Slow decay, if any (사라지지 않을지도 모름)
- 연구 중에는 실제로 사라지지 않지만 해당 기억과 연결하는 시냅스가 끊어져서 기억이 안 나는 것일 수도 있다.
- Huge or unlimited capacity
- Two types
- Explicit memories are declarative memories, include all of the memories that are available in consciousness
- Episodic memory & Semantic memory
- Implicit memories are those that are mostly unconscious
- Procedural memory & Emotional memory
- 의식적으로 기억하지 않는, 글씨 쓸 때 펜을 어떻게 잡고 있고 어떻게 쓰고 있는지 생각 안 하는 것처럼
- Explicit memories are declarative memories, include all of the memories that are available in consciousness
Long-term Memory (cont.)
- Explicit memories
- Episodic: serial memory of events (일어났던 사건을 기억하는)
- Semantic: structured memory of facts, concepts, skills (역할을 기억하는)
- Semantic LTM derived from episodic LTM
- Implicit memories
- Procedural: the use of objects or movements of the body, such as how exactly to use a pencil or ride a bicycle
- Emotional: the memory for events that evoke a particularly strong emotion
- Semantic memory structure
- Provides access to information
- Represents relationships between bits of information
- Supports inference
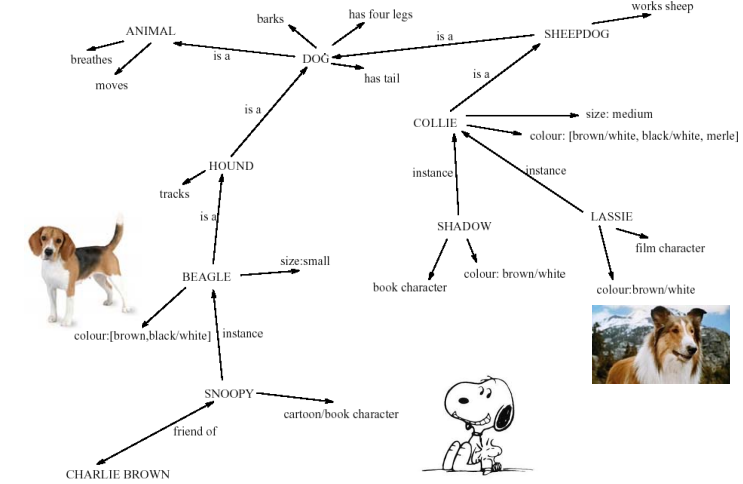
- Model: Semantic Network
- Inheritance – child nodes inherit properties of parent nodes
- Explicit relationships between bits of information
- Supports inference through inheritance
LTM - Semantic Network
Models of LTM - Frames
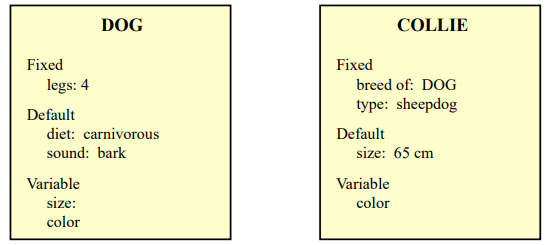
- Information organized in data structures
- Slots in structure instantiated with values for instance of data
- Type–subtype relationships
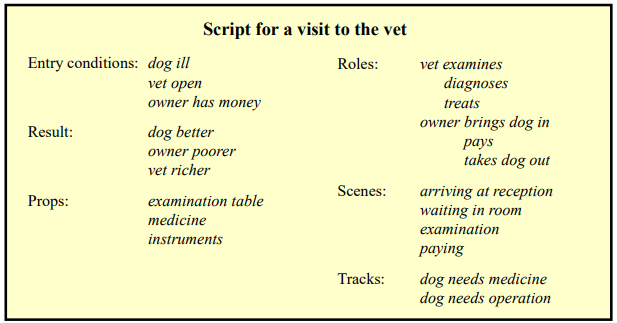
Models of LTM - Scripts
- Model of stereotypical information required to interpret situation
- Script has elements that can be instantiated with values for context
- 수의사를 만나러 가는 스크립트
Models of LTM - Production Rules
- Representation of procedural knowledge.
- Condition/action rules
- if condition is matched
- then use rule to determine action

LTM - Storage of information
- Rehearsal
- Information moves from STM to LTM
- Total time hypothesis
- Amount retained proportional to rehearsal time
- Distribution of practice effect
- Optimized by spreading learning over time
- Structure, meaning and familiarity
- Information easier to remember
LTM - Forgetting
- Decay
- Information is lost gradually but very slowly
- Interference
- New information replaces old: retroactive interference
- Old may interfere with new: proactive inhibition
- So may not forget at all memory is selective …
- Affected by emotion
- Can subconsciously ‘choose’ to forget
LTM - Retrieval
- Recall
- Information reproduced from memory can be assisted by cues, e.g. categories, imagery
- Recognition
- Information gives knowledge that it has been seen before
- Less complex than recall - information is cue*(recall과의 차이)
Types of Human Memory: by Luke Mastin

댓글남기기