[HCI] 3. Computer
The Computer
- a computer system is made up of various elements
- each of these elements affects the interaction
- input devices – text entry and pointing
- output devices – screen (small&large), digital paper
- virtual reality – special interaction and display devices
- physical interaction – e.g. sound, haptic, bio-sensing
- paper – as output (print) and input (scan)
- memory – RAM & permanent media, capacity & access
- processing – speed of processing, networks
Interacting with computers
to understand human–computer interaction … need to understand computers!
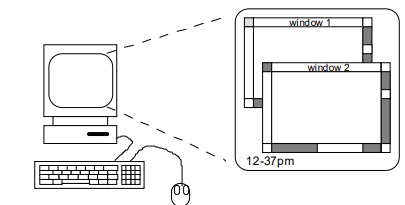
A ‘typical’ computer system
- screen, or monitor, on which there are windows
- keyboard
-
mouse/trackpad
- variations
- desktop
- laptop
- tablet
- the devices dictate(구술하다) the styles of interaction that the system supports
- If we use different devices, then the interface will support a different style of interaction
How many computers …
-
in your house?
- PC
- TV, VCR, DVD, HiFi, cable/satellite TV
- microwave, cooker, washing machine
- central heating
- security system
-> can you think of more?
-
in your pockets?
- tablet
- phone, camera
- smart card, card with magnetic strip?
- electronic car key
- USB memory
-> try your pockets and bags
Interactivity?
- Long ago in a galaxy far away … batch processing
- punched card stacks or large data files prepared
- long wait ….
- line printer output
- … and if it is not right …
- Now most computing is interactive
- rapid feedback
- the user in control (most of the time)
- doing rather than thinking …
- Is faster always better?
text entry devices: Keyboards
- Most common text input device
- Allows rapid entry of text by experienced users
- Keypress closes circuit connection, causing a character code to be sent
- Usually connected by cable, but can be wireless
Layout - QWERTY
- Standardised layout
- but …
- non-alphanumeric keys are placed differently
- 영숫자가 다르게 배치됨
- accented symbols needed for different scripts
- 다른 스크립트에 필요한 악센트 기호
- minor differences between UK and USA keyboards
- non-alphanumeric keys are placed differently
- QWERTY arrangement not optimal for typing
- layout to prevent typewriters jamming! (그래서 많이쓰고 연속되는 키가 바로 옆에 있지 않다.)
- Alternative designs allow faster typing but large social base of QWERTY typists produces reluctance(꺼림칙) to change.
- 바꾸고 싶은데 쿼티에서 바꾼다고…? 꺼림칙…

Alternative keyboard layouts
- Alphabetic
- keys arranged in alphabetic order
- not faster for trained typists
- not faster for beginners either!
- Dvorak
- common letters under dominant fingers
- biased towards right hand
- common combinations of letters alternate between hands
- 10-15% improvement in speed and reduction in fatigue
- But - large social base of QWERTY typists produce market pressures not to change
Special keyboard

- One-handed keyboard
- designs to reduce fatigue for RSI
- e.g. the Maltron left-handed keyboard
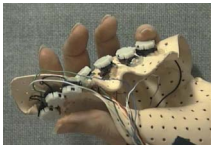
- Chord keyboard
- letters typed as combination of keys pressed simultaneously
- BUT - social resistance, plus fatigue after extended use
- NEW – niche market for some wearables
Phone pad and T9 entry

- use numeric keys with multiple presses

- hello = 4433555[pause]555666
- surprisingly fast!
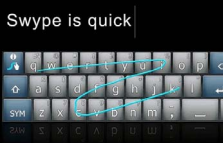
- T9 predictive entry
- type as if single key for each letter
- use dictionary to ‘guess’ the right word
- hello = 43556 …
- but 26 -> menu ‘am’ or ‘an’
Handwriting recognition
- Text can be input into the computer, using a pen and a digitizing tablet
- natural interaction
- Technical problems:
- capturing all useful information - stroke path, pressure, etc. in a natural manner
- segmenting joined up writing into individual letters
- interpreting individual letters
- coping with different styles of handwriting
- Used in smartphones, and tablet computers … … leave the keyboard on the desk!
Speech recognition
- Improving rapidly
- Most successful when:
- single user – initial training and learns peculiarities (특이점)
- limited vocabulary systems
- Problems with
- external noise interfering
- imprecision of pronunciation
- large vocabularies
- different speakers
Scanners
- Take paper and convert it into a bitmap
- Two sorts of scanner
- flat-bed: paper placed on a glass plate; whole page converted into bitmap
- hand-held: scanner passed over paper, digitising strip typically 3-4” wide. some camera apps do the same.
- Shines light at paper and note intensity of reflection
- colour or greyscale
- Typical resolutions from 600–2400 dpi
Optical character recognition
- OCR converts bitmap back into text
- different fonts
- create problems for simple “template matching” algorithms
- more complex systems segment text, decompose it into lines and arcs, and decipher characters that way
- page format
- columns, pictures, headers and footers
Positioning, pointing and drawing: the Mouse

- Handheld pointing device
- very common & easy to use
- Two characteristics
- planar movement
- Buttons : usually from 1 to 3 buttons on top, used for making a selection, indicating an option, or to initiate drawing etc.
- Relative movement only is detectable.
- Movement of mouse moves screen cursor
- … an indirect manipulation device.
- device itself doesn’t obscure(모호하다) screen, is accurate and fast.
- hand-eye coordination problems for novice(초심자) users
Trackball and thumbwheels

- Touchpad
- small touch sensitive tablets
- ‘stroke’ to move mouse pointer
- used mainly in laptop computers
- Trackball
- ball is rotated inside static housing
- like an upside-down mouse!
- relative motion moves cursor
- indirect device, fairly accurate
- separate buttons for picking
- very fast for gaming
- used in some portable and notebook computers.
- Thumbwheels …
- for accurate CAD – two dials for X-Y cursor position
- for fast scrolling – single dial on mouse
Joystick and Pointing Stick

-
Joystick
-
indirect
pressure of stick = velocity of movement
-
buttons for selection
on top or on front like a trigger
-
often used for computer games
aircraft controls and 3D navigation
-

- Pointing Stick
- for laptop computers
- miniature joystick in the middle of the keyboard
Digitizing tablet

- Mouse like-device with cross hairs
- used on special surface
- rather like stylus
- very accurate
- used for digitizing maps
Touch screen
- Detect the presence of finger or stylus on the screen.
- works by interrupting matrix of light beams, capacitance changes or ultrasonic reflections
- direct pointing device
- Advantages:
- fast, and requires no specialised pointer
- good for menu selection
- suitable for use in hostile environment: clean and safe from damage.
- Disadvantages:
- finger can mark screen
- imprecise (finger is a fairly blunt(무딘) instrument(도구)!)
- difficult to select small regions or perform accurate drawing
- lifting arm can be tiring
Eyegaze
- Control interface by eye gaze direction
- e.g. look at a menu item to select it
- Uses IR laser reflected off retina (망막)
- … a very low power laser!
- Mainly used for evaluation
- Potential for hands-free control
- High accuracy requires headset
- Cheaper and lower accuracy devices available
- Sit under the screen like a small webcam

Display devices: Resolution and colour depth
- Resolution … used (inconsistently) for
- number of pixels on screen (width x height)
- e.g. SVGA 1024 x 768, Full HD 1920 x 1080
- density of pixels (in pixels or dots per inch - dpi)
- typically between 72 and 96 dpi, for retina 200 to 400 dpi
- number of pixels on screen (width x height)
- Aspect ratio
- ration between width and height
- 4:3 for computer screens, 16:9 for wide-screen TV
- Colour depth:
- how many different colours for each pixel?
- black/white or greys only
- 256 from a palette
- 8 bits each for red/green/blue = millions of colours
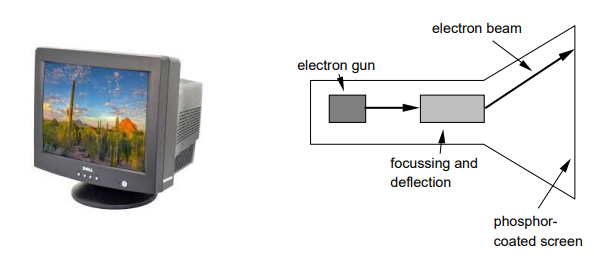
Cathode ray tube(CRT)
- Stream of electrons emitted from electron gun, focused and directed by magnetic fields, hit phosphor-coated screen which glows
- used in TVs and computer monitors
Liquid crystal displays (LCD)
- Smaller, lighter, and … no radiation problems.
- Found on phones, portables and notebooks, … and increasingly on desktop and for home TV
- also used in dedicated displays: digital watches, mobile phones, HiFi controls
- How it works …
- Top plate transparent and polarised(편광의), bottom plate reflecting or transparent.
- Voltage applied to crystal changes polarisation(편광) and hence colour
- Light reflected not emitted => less eye strain(부담)
- For a device with an internal light source has a backlight
LCD Operating Principle
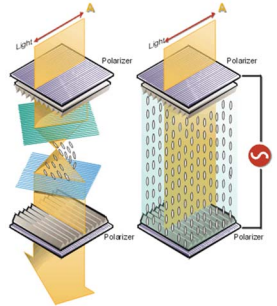
- Online
- Surrounding light is polarized on the upper plate.
- Molecules and lights are parallel to the lower analyzer.
- Light passes through the plate.
- Offline
- Surrounding light is polarized on the upper plate.
- Molecules and lights are perpendicular to the lower analyzer.
- Light cannot pass through the plate.
Digital paper
- what?
- thin flexible sheets
- updated electronically
- but retain display
- how?
- small spheres turned
- or channels with coloured liquid and contrasting spheres
- or move up and down B/W microballs (e-ink)
- 소비전력이 낮음
- rapidly developing area
Virtual reality and 3D interaction: 3D displays
- Desktop VR
- Ordinary screen, mouse or keyboard control
- Perspective and motion give 3D effect
- Seeing in 3D
- Use stereoscopic vision
- VR helmets
- Screen plus shuttered specs, etc

VR motion sickness
- Time delay
- move head … lag … display moves
- conflict: head movement vs. eyes
- Depth perception
- headset gives different stereo distance
- but all focused in same plane
- conflict: eye angle vs. focus
- Conflicting cues => sickness
- helps motivate improvements in technology
Simulators and VR caves
- Scenes projected on walls
- Realistic environment
- Hydraulic(유얍) rams!
- Real controls
- Other people

Dedicated displays
- Analogue representations:
- dials, gauges, lights, etc.
- Digital displays:
- small LCD screens, LED lights, etc.
- Head-up displays (HUD)
- found in aircraft cockpits(콕콕) or automobiles
- show most important controls … depending on context
- Hologram
- Gatebox animated robot

Printing
- image made from small dots
- allows any character set or graphic to be printed,
- critical features:
- resolution
- size and spacing of the dots
- measured in dots per inch (dpi)
- speed
- usually measured in pages per minute
- cost!!
- resolution
Types of dot-based printers
- dot-matrix printers (가끔 영수증 뽑는 데서 보임)
- use inked ribbon (like a typewriter)
- line of pins that can strike the ribbon, dotting the paper.
- typical resolution 80-120 dpi
- ink-jet and bubble-jet printers
- tiny blobs of ink sent from print head to paper
- typically 300 dpi or better .
- laser printer
- like photocopier: dots of electrostatic charge deposited on drum, which picks up toner (black powder form of ink) rolled onto paper which is then fixed with heat
- typically 600 dpi or better.
Processing and networks: Finite processing speed
- Designers tend to assume fast processors, and make interfaces more and more complicated
- But problems occur, because processing cannot keep up with all the tasks it needs to do
- cursor overshooting because system has buffered keypresses
- icon wars - user clicks on icon, nothing happens, clicks on another, then system responds and windows fly everywhere
- Also problems if system is too fast
- e.g. help screens may scroll through text much too rapidly to be read
Moore’s law
- computers get faster and faster!
- 1965 …
- Gordon Moore, co-founder of Intel, noticed a pattern
- processor speed doubles every 18 months
- PC … 1987: 1.5 Mhz, 2002: 1.5 GHz
- similar pattern for memory
- but doubles every 12 months!!
- hard disk … 1991: 20Mbyte : 2002: 30 Gbyte
- baby born today
- record all sound and vision
- by 70 all life’s memories stored in a grain of dust!
The myth of the infinitely fast machine
- implicit assumption … no delays
- an infinitely fast machine
- what is good design for real machines?
- good example … the telephone :
- type keys too fast
- hear tones as numbers sent down the line
- actually an accident of implementation
- emulate in design
Limitations on interactive performance
bottleneck
- Computation bound
- Computation takes ages, causing frustration for the user
- Storage channel bound
- Bottleneck in transference of data from disk to memory
- Graphics bound
- Common bottleneck: updating displays requires a lot of effort sometimes helped by adding a graphics coprocessor optimised to take on the burden
- Network capacity
- Many computers networked – shared resources and files, access to printers etc. – but interactive performance can be reduced by slow network speed
Networked computing
- Networks allow access to …
- large memory and processing
- other people (groupware, email)
- shared resources – esp. the web
- Issues
- network delays – slow feedback
- conflicts – many people update data
- unpredictability
The internet
- history …
- 1969: DARPANET US DoD, 4 sites
- 1971: 23; 1984: 1000; 1989: 10000
- common language (protocols):
- TCP – Transmission Control protocol
- lower level, packets (like letters) between machines
- IP – Internet Protocol
- reliable channel (like phone call) between programs on machines
- email, HTTP, all build on top of these
- TCP – Transmission Control protocol

댓글남기기