[HCI] 7. Development Methodology
HCI Development Methodology
- Roadmap
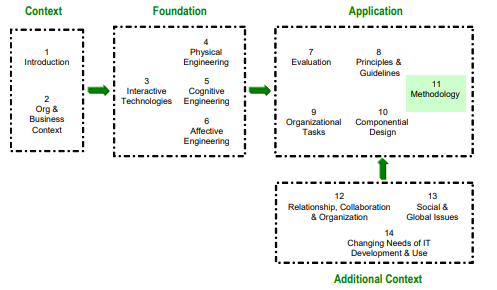
HCI Methodology
-
System Development Methodology:
a standardized development process that defines a set of activities, methods and techniques, best practices, deliverables, and automated tools that systems developers and project managers are to use to develop and continuously improve information systems
The Role of HCI Development in SDLC
- System Development Philosophy: follow formal scientific and engineering practice, yet make room for a strong creative element.
- The general principles of user-centered systems development include
- (1) involving users as much as possible
- (2) integrating knowledge and expertise from different disciplines
- (3) encouraging high interactivity
The Role of HCI Development in SDLC
- Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC): a commonly used methodology for information systems development that breaks the whole systems development process into manageable phases.
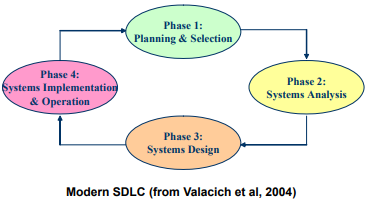
The Role of HCI Development in SDLC
- Iteration through each of the phases and back to the previous phases is key to creating successful systems. Figure below illustrates the importance of iteration.
- small iteration
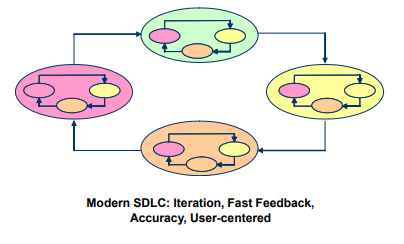
The Human-Centered SDLC Model: HCSDLC
- HCSDLC: a human centered systems development methodology where organizational needs and human needs are considered together throughout the systems development life cycle.
- The next slide depicts the HCSDLC. The left side (a) is a typical SDLC model while the right side (b) is the HCSDLC model that covers both SA&D (System Analysis & Design) and HCI concerns and activities.
The Human-Centered SDLC Model: HCSDLC
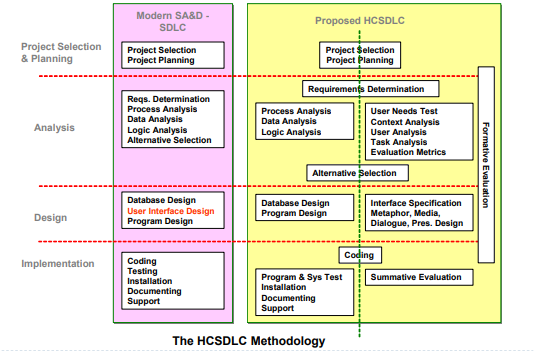
노란 박스 오른쪽 부분은 사람(user)을 위해 고려되는 부분
The HCI Development Methodology
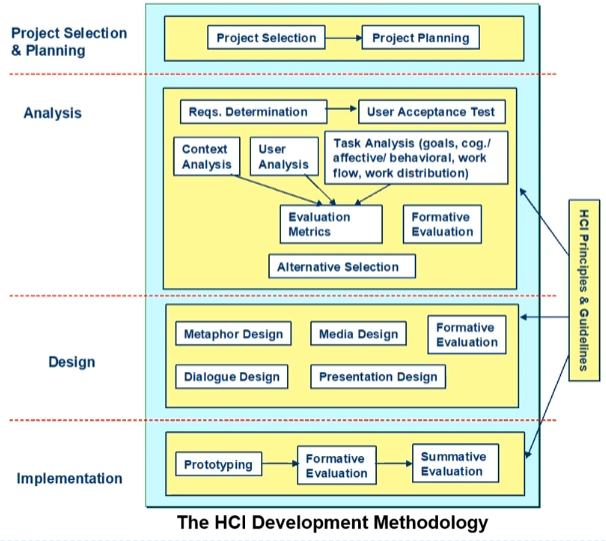
Philosophy, Strategies, Principles and Guidelines
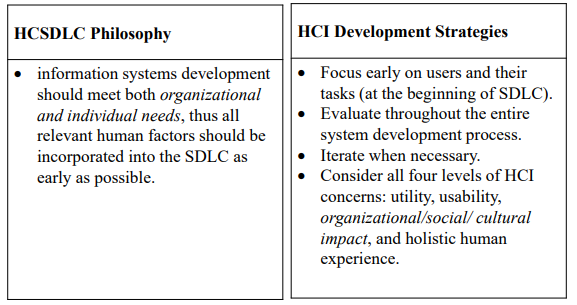
Philosophy, Strategies, Principles and Guidelines
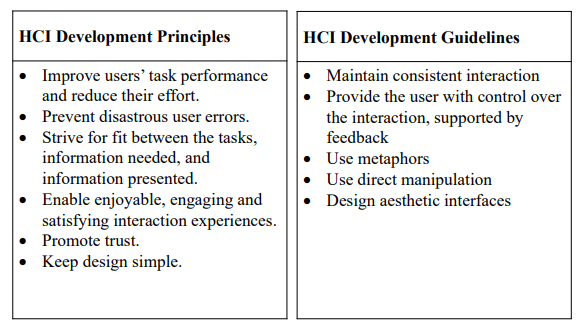
- metaphors가 중요함
- 기억에 의존하지 않고 직관적으로 사용할 수 있도록
The Project Selection and Planning Phase
- Project selection and planning:
- the first phase in SDLC where an organization’s total information systems needs are analyzed and arranged, a potential information systems project is identified, and an argument for continuing or not continuing with the project is presented.
The Project Selection and Planning Phase
- One important activity during project planning is to assess project feasibility(실현가능성). This is also called a feasibility study. Most feasibility factors fall into the following six categories:
- Economic or cost-benefit analysis
- Operational
- Technical
- Schedule
- Legal and contractual
- Political
The Interaction Analysis Phase
- Analysis: studies the current system and proposes alternative systems.
- From the HCI perspective, requirement determination is still one of the most important activities, and alternative generation and selection are also necessary before subsequent design is conducted.
- In addition, HCI analysis includes user-acceptance tests on the system requirements
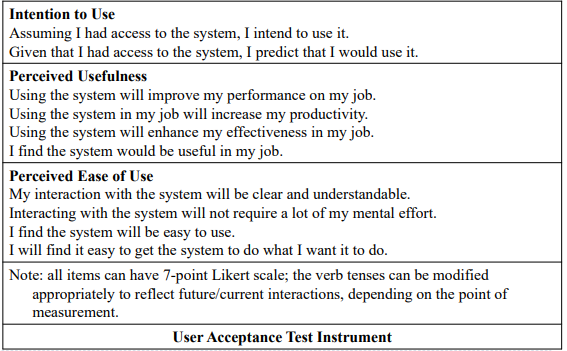
Requirement Determination and User-Acceptance Test
- User acceptance test:
- a test during the analysis stage using simple mock-ups to test the likelihood of the system’s functionalities being accepted by its potential users.
Requirement Determination and User-Acceptance Test
Context Analysis
- Context analysis includes understanding the
technical,environmentalandsocial settingswhere the information systems will be used. - There are four aspects in Context Analysis:
- physical context,
- technical context,
- organizational context, and
- social and cultural context.
- Physical context:
- Where are the tasks carried out?
- What entities and resources are implicated(연루되다) in task operation?
- What physical structures and entities are necessary to understand observed task action?
- Technical context:
- What are the technology infrastructure, platforms, hardware and system software, network/wireless connections?
- For example, an E-commerce website may be designed to only allow people with certain browser versions to access. The website may also be designed to allow small screen devices such as PDAs or mobile phones access.
- Organizational context:
- What is the larger system into which this information system is embedded?
- What are the interactions with other entities in the organization?
- What are the organizational policies or practices that may affect the individual’s attitude and behavior towards using the system?
- Social and cultural context:
- What are the social or cultural factors that may affect user attitudes and eventual use of the information system?
- Any information system is always part of a larger social system.
User Analysis
- User Analysis:
identifies the target users of the system and their characteristics.
- Demographic data
- Traits and intelligence
- Job or task related factors
Task analysis
- Task Analysis: studies what and how users think and feel when they do things to achieve their goals.
- Possible points of analysis in task analysis
- User goals and use cases
- Cognitive, affective, and behavioural analysis of user tasks
- Workflow analysis
- General work distribution between users and the website/machine
Evaluation Metrics
- Evaluation Metrics: specifies the expected human-computer interaction goals of the system being designed. There are four types of HCI goals.
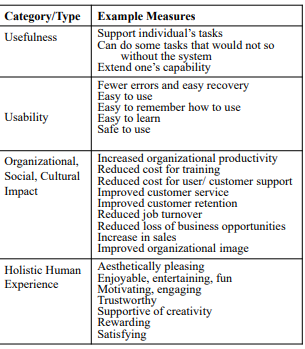
usefulness
Usability
Organizational
Holistic: 만족스러운
Alternative Generation and Selection
- Although SA&D emphasizes functionality in selecting design strategies, the approach of generating and selecting best alternatives can also be applied to HCI design strategies. The deliverables(성과물) include
- (1) three substantially different design strategies (low, middle, and high range)
- (2) a design strategy judged most likely to lead to the most desirable system
- 가장 바람직한 시스템으로 이어질 가능성이 가장 높은 것으로 판단되는 설계 전략
The Interaction Design Phase
- Design: to create or construct the system according to the analysis results.
- Interface specification includes semantic understanding of the information needs to support HCI analysis results, and syntactical and lexical decisions including metaphor, media, dialogue, and presentation designs.
- 인터페이스 사양에는 HCI 분석 결과를 지원하기 위한 정보 필요성에 대한 의미론적 이해와 은유, 미디어, 대화 및 프레젠테이션 설계를 포함한 구문 및 어휘적 결정이 포함된다.
The Interaction Design Phase
- Metaphor and visualization design helps the user develop a mental model of the system.
- It is concerned with finding or inventing metaphors or analogies that are appropriate for users to understand the entire system or part of it.
- There are well accepted metaphors for certain tasks, such as a shopping cart for holding items before checking out in the E-Commerce context,
- and light bulbs for online help or daily tips in productivity software packages.
The Interaction Design Phase
- Media design is concerned with selecting appropriate media types for meeting the specific information presentation needs and human experience needs.
- Popular media types include text, static images (e.g., painting, drawing or photos), dynamic images (e.g., video clips and animations), and sound.
The Interaction Design Phase
- Dialogue design focuses on how information is provided to and captured from users during a specific task.
- Dialogues are analogous to a conversation between two people.
- Many existing interaction styles, such as menus, form-fill-ins,natural languages, dialog boxes, and direct manipulation, can be used.
The Interaction Design Phase
- Presentation design
- maximize visibility;
- minimize search time;
- provide structure and sequence of display; (grouping)
- focus user attention on key data
- comprehended;
- provide only relevant information; and
- don’t overload user’s working memory(short-term memory).
Formative Evaluations
- Formative evaluations identify defects in designs, thus informing design iterations and refinements.
- A number of different formative evaluations can occur several times during the design stage to form final decisions.
- In fact, it is strongly recommended that formative evaluations occur during the entire HCI development life cycle
The Implementation Phase
- HCI development in this phase includes
- (1) prototyping,
- (2) formative evaluations to fine-tune the system,
- (3) summative evaluation before system release and
- (4) use evaluation after the system is installed and being used by targeted users for a period of time.
- 시스템 설치 후 일정 기간 대상 사용자가 사용 후 평가 사용
Documenting HCI Development Activities and Deliverables
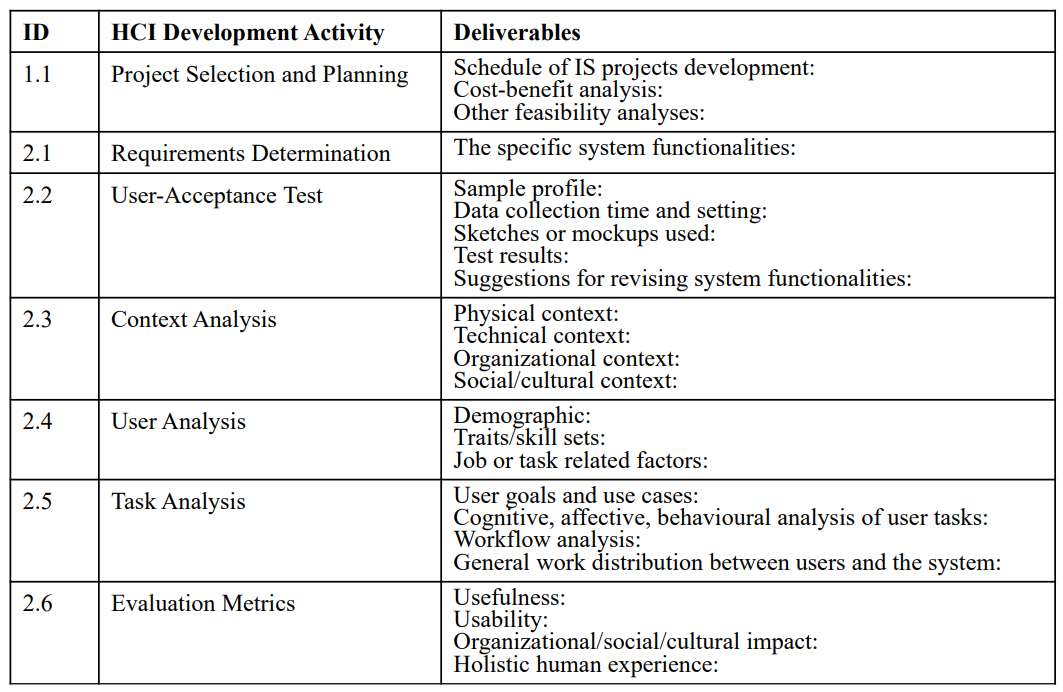
Documenting HCI Development Activities and Deliverables (cont)
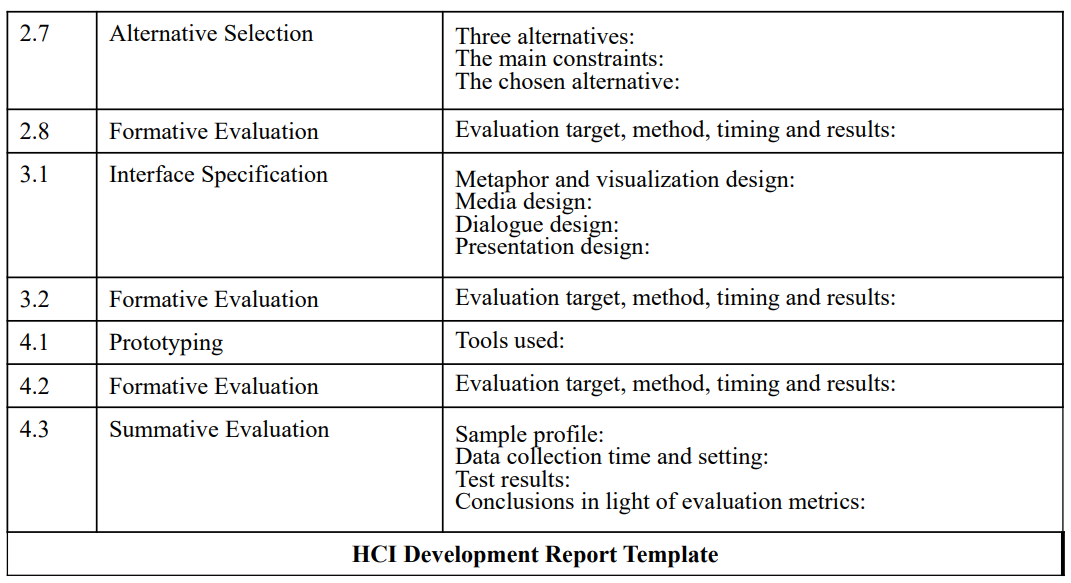
계속되는 evaluation
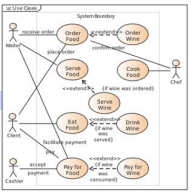
Applying the HCI Development Methodology: e-Gourmet example
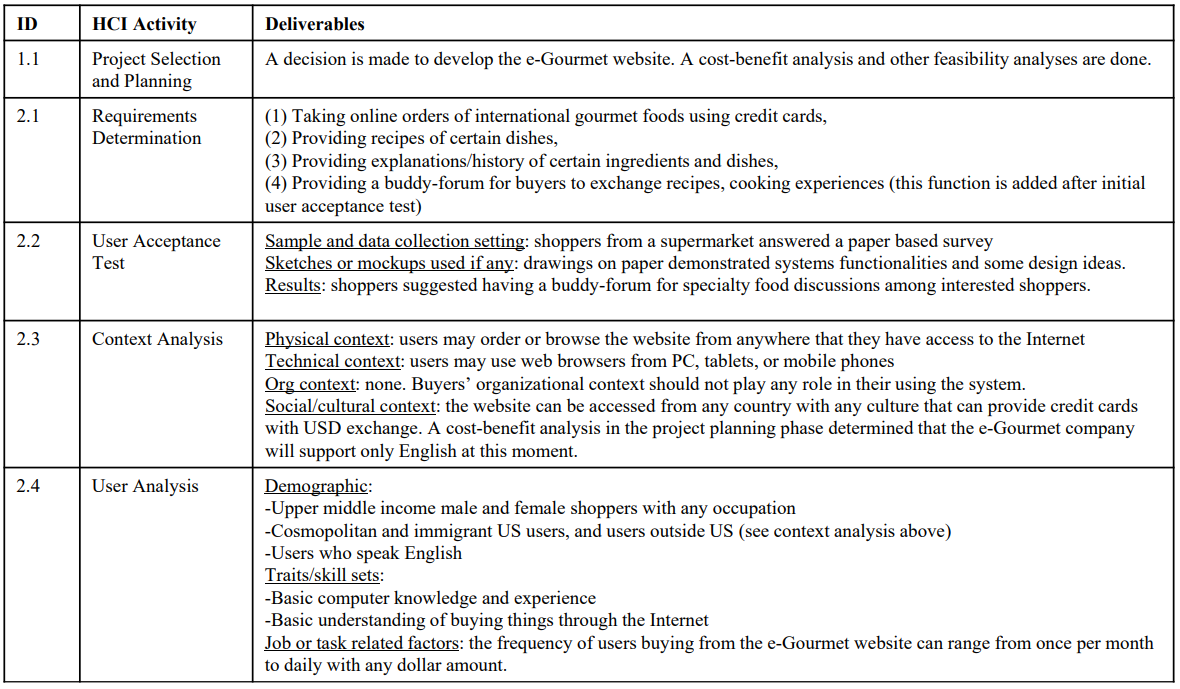
Applying the HCI Development Methodology: e-Gourmet example

case 5: 다른 사람들에게 site를 추천하는 방법
Applying the HCI Development Methodology: e-Gourmet example
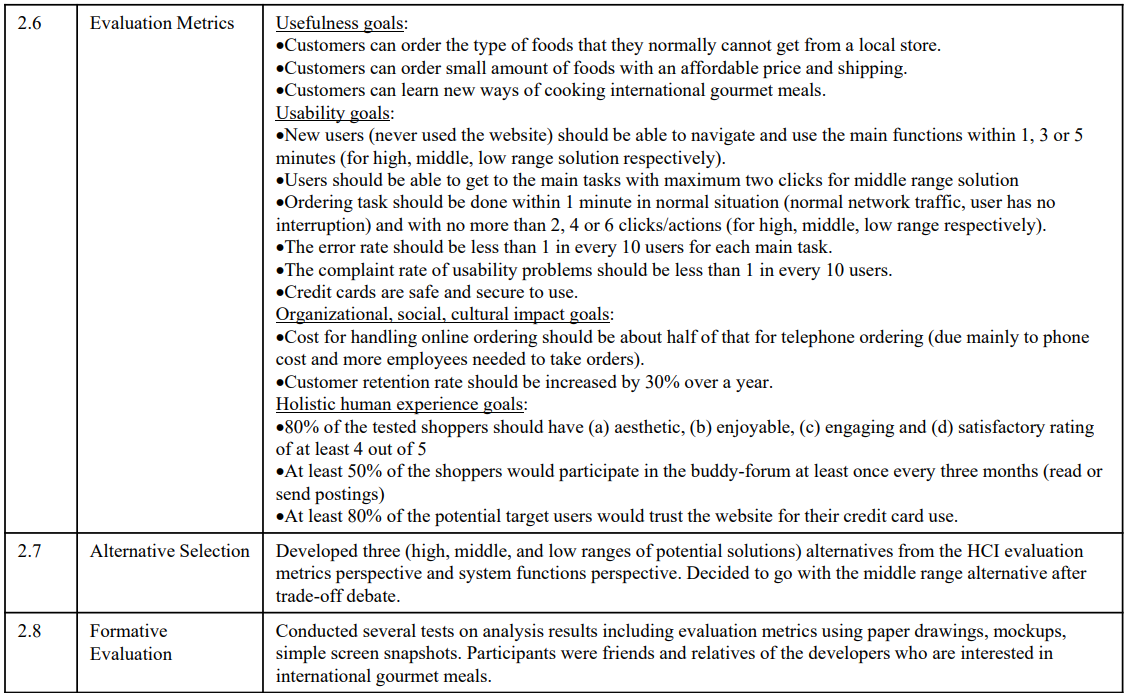
Applying the HCI Development Methodology: e-Gourmet example
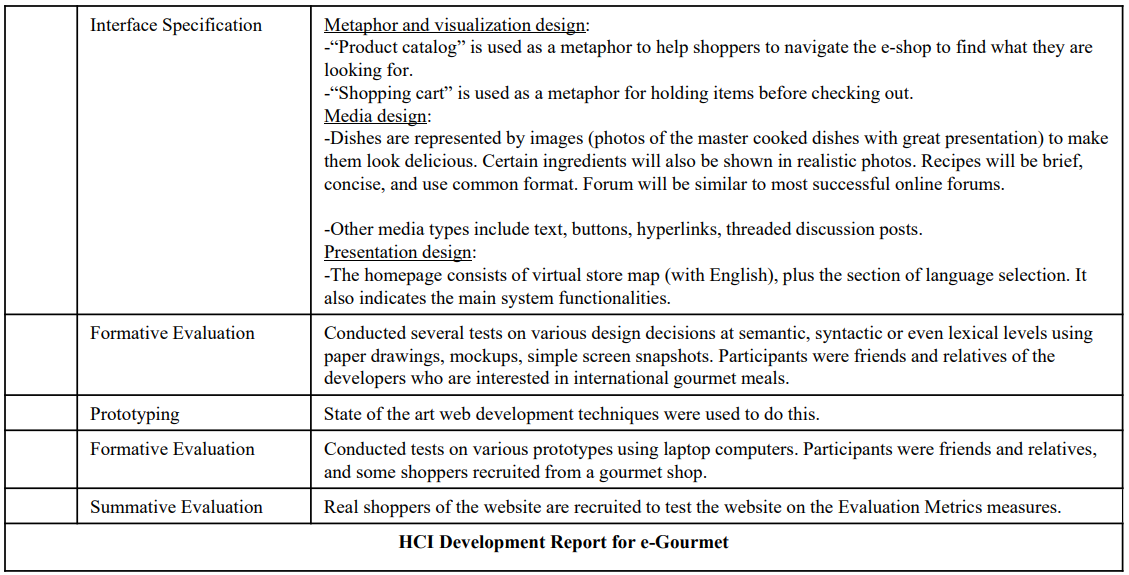
Applying the HCI Development Methodology: e-Gourmet example
- Figure below depicts two possible designs for the top level layout, media selection and presentation design considerations that should help users develop appropriate mental models of the website.
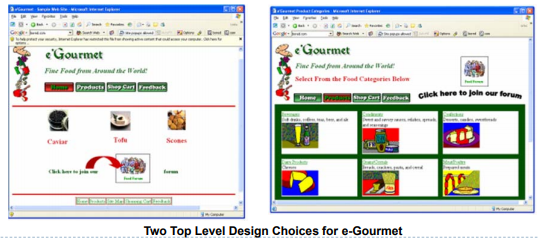
Applying the HCI Development Methodology: e-Gourmet example
- The Figure shows two possible designs for supporting this task.
- The (b) design allows a user to easily navigate the website, (menu가 많으면 navigation이 쉬워짐)
- while the (a) design requires the user to go back to the previous page in order to go to other places of the website. (왔다갔다를 많이 하면 overload 유도)
- Such a small difference in design can cause a big difference in user’s experience in using the website. Having the navigation bar on the page is the result of a workflow analysis during task analysis.
Summary
- This chapter posits the HCI development in the overall system development life cycle by presenting the human-centered SDLC (HCSDLC) model first, and then emphasizes the HCI development aspect.
- HCSDLC is an integrated methodology that emphasizes humancenterednessand considers HCI issues together with SA&D issues throughout the entire system development life cycle.
- The HCI part of the HCSDLC methodology can be used alone to concentrate on the HCI development of an information system.
- In this chapter, we provide very detailed materials on HCI development methodology.
- A HCI Development Report template is used to summarize the activities and deliverables of the methodology.
- Examples are also used to illustrate how to apply the methodology.

댓글남기기