[HCI] 9. Dialogue Notations and Design 2
O/X
short answer
화면에서 HCI적 property를 찾아내고 왜 그런지 설명하고 논리만 맞으면 ok
최대한 많이 쓸 것
textual Notations
- Grammars
- Production rules
- Communication Sequential Process (CSP) and event algebras
Textual - Grammars
- Regular expressionssel-line click click* double-click
- Equivalent expressiveness to JSD
- Good for certain kinds of dialogue such as command line syntax
- BNF (Backus Normal Form)
expr ::= empty
| atom expr
| ‘(‘ expr ‘)’ expr
- More powerful than regular exp. or STNs
- Iteration through recursive definitions
- Still NO concurrent dialogue
(사진 슬라이드)
Production Rules
더 사람 말에 가까움
- Unordered list of rules
- If condition then action
- Conditions: user initiated events and current state
- Actions: response to user or change to system’s state
- E.g. Select-line -> start-line <highlight ‘line’>
- Click start-line -> rest-line <rubber band on>
- Two forms:
- Event based: firing a rule removes its conditions from memory
- State based: memory changed only if action explicitly specifies
- state의 이름만 바꾸면서
- Every rule always potentially active
- Good for concurrency
- Bad for sequence
Event based Production Rules
- if condition then action Sel-line null -> first C-point first -> rest C-point rest -> rest D-point rest -> < draw line >
- Note:
- Events added to list of pending events
- ‘first’ and ‘rest’ are internally generated events
- Bad at state!
- Permanent status information is difficult to represent.
Propositional Production System
- State based
- Attributes:
- Mouse: { mouse-off, select-line, click-point, double-click }
- Line-state: { menu, first, rest }
- Rules (feedback not shown):
- select-line -> mouse-off, first
- click-point, first -> mouse-off, rest
- click-point, rest -> mouse-off, rest
- double-click, rest -> mouse-off, menu
- Bad at events!
Communication Sequential Process (CSP) and Process Algebras
- Used in Alexander’s SPI (Specification, Prototyping and Interaction), and Agent notation
- Good for sequential dialogues
- Bold-tog = select-bold? -> bold-on -> select-bold? ->bold-off -> Bold-tog
- Italic-tog = . . .
- Under-tog = . . .
- And concurrent dialogue
-
Dialogue-box = Bold-tog Italic-tog Under-tog
-
- But causality unclear
Syntactic Dialogue Notations - Summary
- Diagrammatic
- STN, JSD, Flow charts
- Textual
- Grammars, Production rules, CSP
- Issues
- Event based vs. State based
- Power vs. Clarity
- Model vs. Notation
- Sequential vs. Concurrent
Semantics - Alexander SPI (i)
- Two part specification:
- EventCSP - Pure dialogue order
- EventISL - Target dependent semantics
- * ISL: Interaction Specification Language
- Dialogue description – Centralized
- Syntactic/Semantic trade-off – Tolerable
Semantics - Alexander SPI (ii)
- EventCSP Login = login-mess -> get-name -> Passwd Passwd = passwd-mess -> (invalid -> Login [ ] valid -> Session)
- EventISL
event: login-mess prompt: true out: “Login:” event: get-name uses: input set: user-id = input event: valid uses: input, user-id, passwd-db wgen: passwd-id = passwd-db(user-id)
Semantics - Raw Code
- Event loop for word processor
- Dialogue description
- very distributed
- Syntactic/Semantic
trade-off
- terrible!

Action Properties
- Completeness
- Only a subset of the full set of actions are allowed for any state.
- But what about missed actions, not shown on the diagram?
- Unforeseen circumstances: need to know the consequences of all actions under any event and account for them.
- For each state/action pair, the designer ought to decide what the behavior will be.
- Determinism
- Several arcs for one action
- Deliberate: application decision
- Accident: production rules
- e.g. Nested escapes or actions may be dependent on guard conditions
- Consistency
- We expect the same action in different states to do the same effect
- e.g. modes and visibility
Checking Properties (i)
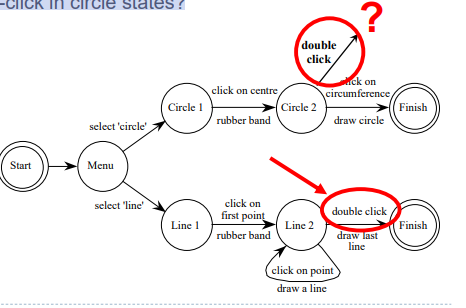
- Completeness
- Double-click in circle states?
State Properties
- Reachability
- Can you get anywhere from anywhere?
- And how easily
- 클릭 몇 번으로 이 state에서 저 state까지 갈 수 있는가
- Reversibility
- Can you get to the previous state?
- But NOT undo (undo랑 다름)
- 이전 state로 다시 가는데 어떤 방식으로 갈 수 있나?
- flow를 따라서
- Dangerous states
- Some states you don’t want to get to
- Some states must be made difficult to reach (disk format !)
- Dangerous states can’t be determined automatically
- The move to dangerous states must be different from other sequences (not-consistent!)
Checking Properties (ii)
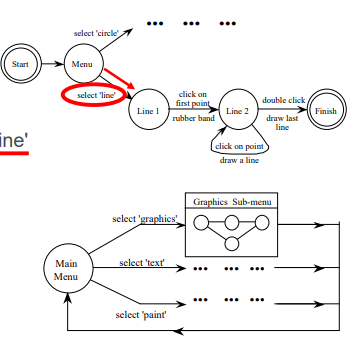
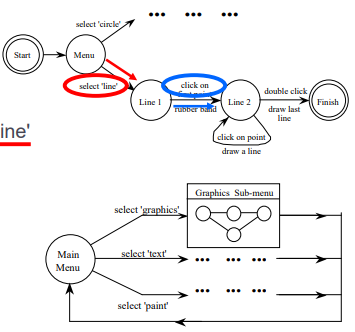
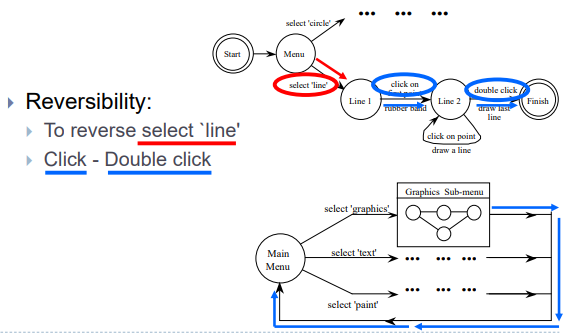
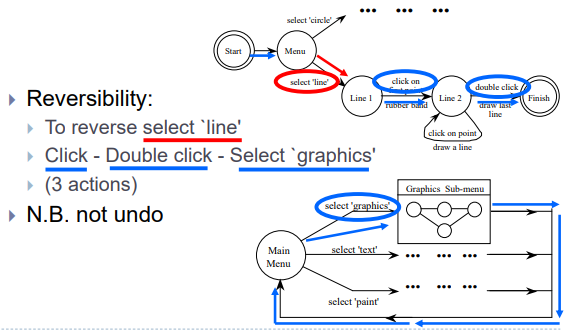
- Reversibility:
- To reverse select `line’
- Click-Double click - Select ‘graphics’
- (3 actions)
- N.B. not undo
- if you want multiple line without leaving this menu?
Checking Properties (ii)
- Reversibility:
- To reverse select `line’
- Click
Checking Properties (ii)
Checking Properties (ii)
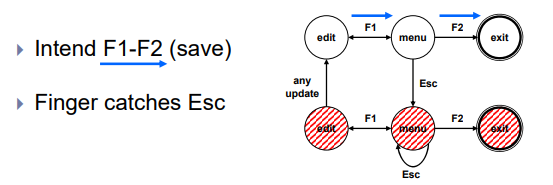
Dangerous States
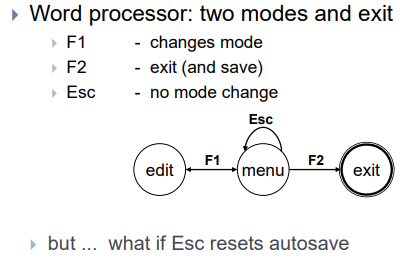
- ESC는 아무 기능이 없는데 만약 autosave를 reset하는 기능을 넣어버렸다면?? (다음 슬라이드에서 설명)
Dangerous States (ii)
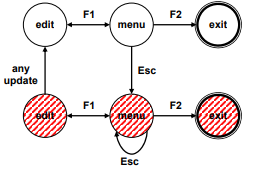
- Exit with/without save => dangerous states
- Duplicate states - semantic distinction
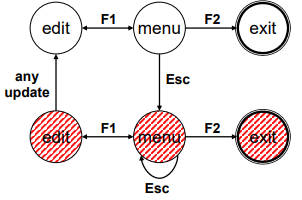
- F1-F2 - exit with save
- F1-Esc-F2 - exit with no save
Lexical Issues
위 예제 처럼 esc에 그런 기능이 있으면 합리적으로 보이나 몇 가지 문제가 있음
- Visibility
- Differentiate modes and states
- save를 하고 나갈 수 있는지 save를 못하고 나갈 수 있는지 알 수 있는 방도가 있는지
- 즉, esc가 눌렸었는지 check가 되나
- save를 하고 나갈 수 있는지 save를 못하고 나갈 수 있는지 알 수 있는 방도가 있는지
- Annotations to dialogue
- Differentiate modes and states
- Style
- Command based- verb noun (e.g. delete files)
- Mouse based - noun verb (e.g. move files to trashcan)
- 이런 consistency가 마구 섞여 있으면 dangerous state로 넘어갈 여지를 많이 남기는 것
- Layout
- Not just appearance …
Layout Matters
- Word processor - Dangerous states
- Old keyboard - OK
- 멀리 떨어져 있음
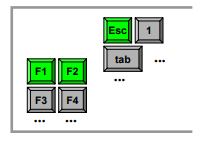
- New keyboard layout
- esc가 구석이 있긴 한데 바로 옆에 function키가 바로 옆에 있음…
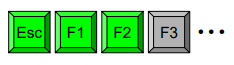
- New keyboard layout
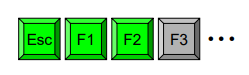
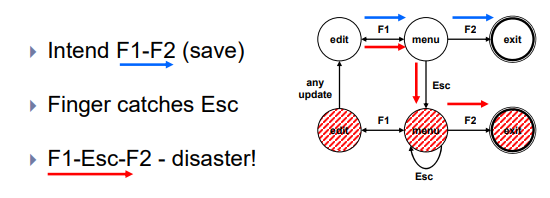
Dialogue Analysis - Summary
- Semantics and dialogue
- Attaching semantics
- Distributed/centralized dialogue description
- Maximizing syntactic description
- Properties of dialogue
- Action properties: completeness(또 다른 방법 있는지), determinism(분기), consistency
- State properties: reachability(도달 할 수 있는 state를 만들고 있는지), reversibility, dangerous states
- Presentation and lexical issues
- Visibility, style, layout
- N.B. not independent of dialogue
Digital Watch – User Instructions
- Two main modes
- Limited interface
- 3 buttons:
A, Up, Down
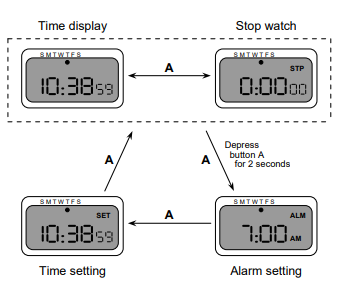
- 3 buttons:
A, Up, Down
- Button A
- Changes mode
- Button Up/Down
- Changes Time/Alarm
Digital Watch – User Instructions
- Dangerous states
- Unintended setting
- Guarded …by two second hold
- Completeness
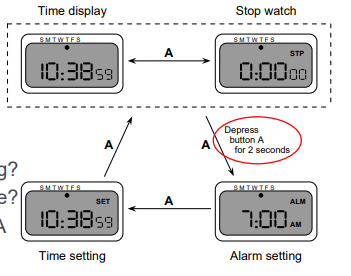
- From where to setting?
- From setting to where?
- Distinguish depress A and release A(2초 동안 누르면 어떻게 됨?)
- What do they do in all modes?
Digital Watch – Designers Instructions
- and …
- That’s just one button to change modes
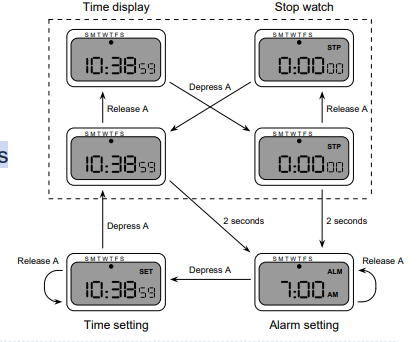
눌렀다 놓기 -> stop watch
누른 상태에서 2초 버티면 알람 setting으로
- 알람 상태에서 2초 버텨도 time setting으로 넘어감
dialog로 설계한 예제임(dangerous 고려, 등등)

댓글남기기