[HCI] 9. Dialogue Notations and Design 1
Dialogue Notations and Design
- Dialogue Notations
- Diagrammatic(그림으로 그릴 수 있는)
- State transition networks, JSD (Jackson Structured Design) diagrams, Flow charts(플로우차트)
- Textual(텍스트 형식)
- Formal grammars, Production rules, CSP (Communication Sequential Process)
- Diagrammatic(그림으로 그릴 수 있는)
- Dialogue linked to
- The semantics of the system – what it does
- The presentation of the system – how it looks
- Formal descriptions can be analyzed
- For inconsistent actions
- For difficult to reverse actions
- For missing actions
- For potential miskeying errors(엉뚱한 거 잘못눌러서 생기는 error)
What is dialogue?
- Conversation between two or more parties
- Usually cooperative
- In user interfaces
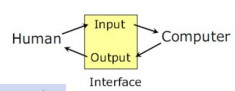
- Refers to the structure of the interaction
- Syntactic level of human–computer ‘conversation’
- Levels
- Lexical (어휘)– shape of icons, actual keys pressed
- Syntactic – order of inputs and outputs(어떤 순서로 눌러야 dialogue가 나오는지)
- Semantic – effect on internal application/data
Structured Human Dialogue
- Human-computer dialogue is very constrained
- Some human-human dialogue is formal too …
- 사람과 사람의 대화도 fix 되어 있는 경우가 있음

(marriage dialogue)
Lessons about Dialogue
- Wedding service
- Sort of script for three parties
- Specifies order
- Some contributions fixed – “I do”
- 몇몇은 고정된 말
- Others variable – “do you man’s name …”
- 사람 이름은 변수로 작용(사람마다 이름을 다르게 불러야 하기 때문에)
- Instructions for ring concurrent with saying words “with this ring …”
- If you say these words, are you married?
- Only if in the right place, with marriage licence
- Syntax is not semantics
- syntax가 지켜진다고 해도 semantic이 맞지 않으면 동작하지 않는 것
… and more(예외 사항)
- What if woman says “I don’t”?
- Real dialogues often have alternatives:

- The process of the trial depends on the defendants response
- Focus on normative responses
- Doesn’t cope with judge saying “off with her head”
- 머리를 날려버려와 같은 말을 할 수 있는 것도 아니고…
- Or in computer dialogue user standing on keyboard!
- Doesn’t cope with judge saying “off with her head”
Dialogue Design Notations
- Dialogue gets buried in the program
- 프로그램 안 쪽에 깊이 있을 것임
- In a big system can we:
- Analyse the dialogue:
- e.g. Can the user always get to see current shopping basket
- Change platforms
- e.g. migration from Windows to Mac
- Dialogue notations helps us to
- Analyse systems
- Separate lexical from semantic (어휘와 의미 분류)
- Analyse the dialogue:
- … and before the system is built
- Notations help us understand proposed designs
Graphical Notations
- State-Transition Nets (STN)
- Petri Nets
- State Charts
- Flow Charts
- Jackson Structured Design (JSD) Diagrams
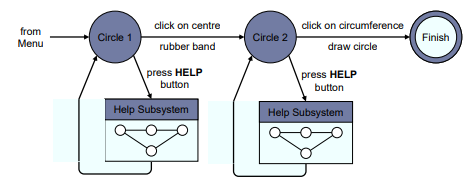
State Transition Networks (STN)
- Circles - states
- Arcs – actions (output) / events (input)
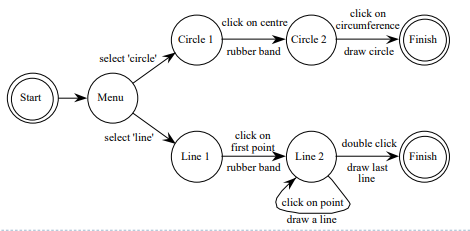
rubber band - 고무줄
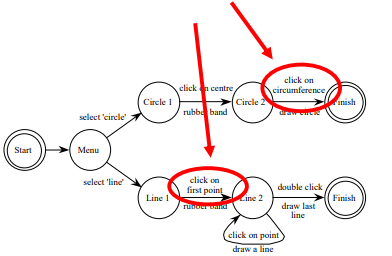
State Transition Networks - Events
- Arc labels a bit cramped because:
- Notation is ‘state heavy’
- The events require most detail
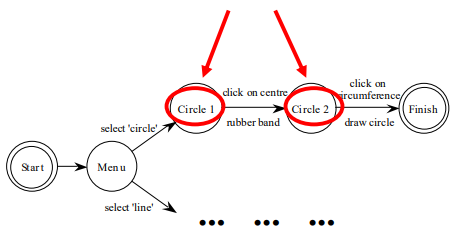
State Transition Networks - States
- Labels in circles a bit uninformative:
- States are hard to name
- But easier to visualise
state가 unique하지 않고 state가 10개쯤 나오는 경우가 생기면 이름 짓기가 어려움
- 비슷한 종류의 작업이 있어도 이름을 다르게 해야하기 때문
Example: Bottle Dispense STN

H state: history
Hierarchical STNs
- Managing complex dialogues
- Named sub-dialogues
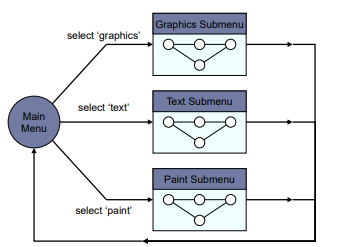
Strengths and Limitations
- Strengths
- Easy to interpret
- Allows choice and iteration to be modelled.
- Limitations
- Concurrent dialogue(왜 문제? - 아래에서 나옴)
- Unusual actions (esc, help)
Concurrent dialogues - ISimple dialogue box
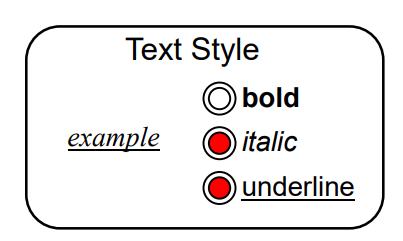
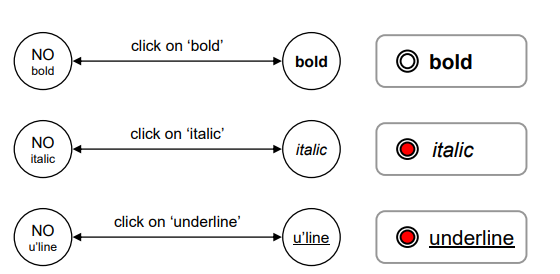
Concurrent dialogues - IIThree toggles - Individual STNs
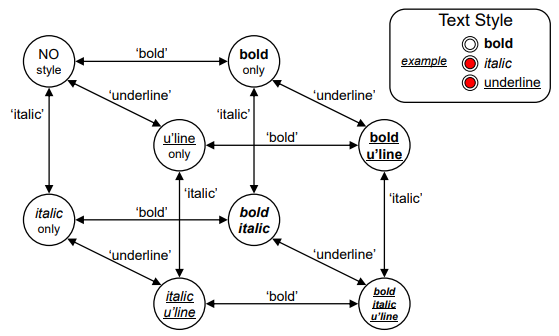
Concurrent dialogues - III Bold and Italic combined
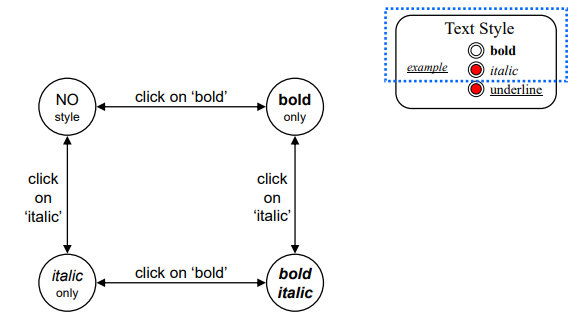
Concurrent dialogues - IV All together - Combinatorial explosion
Escapes
- ‘Back’ in web, escape/cancel keys
- Similar behavior everywhere
- End up with spaghetti of identical behaviors
- Try to avoid this
- e.g. on high level diagram
- ‘Normal’ exit foreach submenu
- Separateescape arc active‘everywhere’ in submenu

Help menus
- Similar problems
- Nearly the same everywhere
- But return to same point in dialogue
- Could specify on STN … but very messy
- Usually best added at a ‘meta’ level
Petri Nets
- One of the oldest notations in computing!
- A simple model of active behavior
- Provide a graphical explanation for easy understanding.
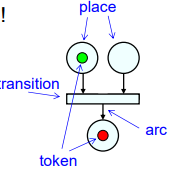
- Four elements of Flow graph:
- Places: Used to symbolize passive elements of the reactive system. A place is represented by a circle.
- Transitions: Used to symbolize active elements of the reactive system. Transitions are represented by squares/rectangles.
- Arc: Used to represent causal relations. Arc is represented by arrows.
- Token: Sit on places (current state). Subject to change. Tokens are represented by small filled circles.
- 토큰이 네트워크 안을 돌아다님
- 토큰을 주고 받는 형태로 일을 한다.(토큰이 있는 곳이 현재 state)
Role of a Token
- A physical object, for example a product, a part, a drug, a person
- An information object, for example a message, a signal, a report
- A collection of objects, for example a truck with products, a warehouse with parts, or an address file
- An indicator of a state, for example the indicator of the state in which a process is, or the state of an object
- An indicator of a condition: the presence of a token indicates whether a certain condition is fulfilled
- Several tokens allowed: Concurrent dialogue states
Role of a Place
- A type of communication medium, like a telephone line, a middleman, or a communication network
- A buffer: for example, a depot, a queue or a post bin
- A geographical location, like a place in a warehouse, office or hospital
- A possible state or state condition: for example, the floor where an elevator is, or the condition that a specialist is available
Role of a Transition
- An event (e.g., starting an operation, the switching of a traffic light from red to green)
- A transformation of an object, like adapting a product, updating a database, or updating a document
- A transport of an object: for example, transporting goods, or sending a file
Construction Rules
- Connections are directed(방향성이 존재)
- No connections between two places or two transitions is allowed
- place와 place, transition과 transition끼리 연결될 수는 없음
- 반드시 transition을 거쳐서 place로 가야됨.
- Places may hold zero or more tokens
- A transition is enabled if each of its input places contains at least one token
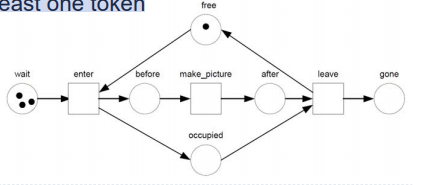
leave transition
각각에 하나씩 하나 이상의 토큰이 있어야 동작
enter: photographer가 프리이고 customer가 before로 갈 때
Petri Net example
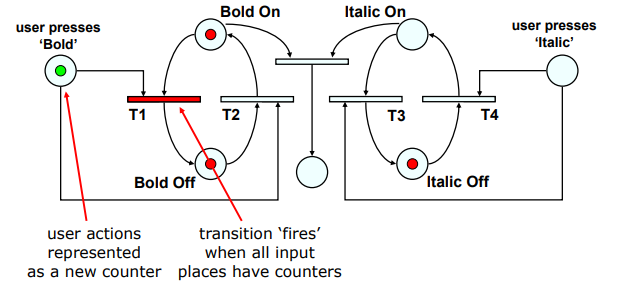
bold on에서 bold off로 토큰이 넘어감.
Example: In a Restaurant
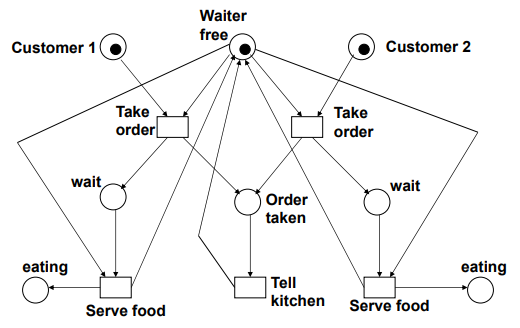
waiter가 free여야 customers가 order를 받을 수 있음
Example: In a Restaurant (Scenarios)
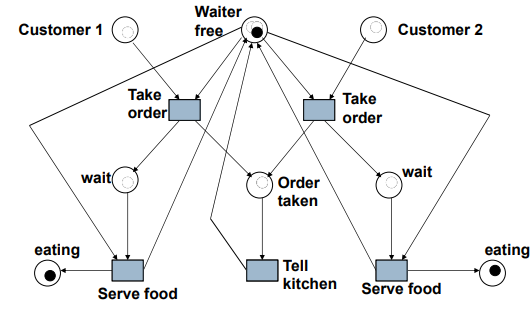
- Scenario 1:
- Start
- -> Waiter takes order from customer 1
- -> serves customer 1
- -> takes order from customer 2
- -> serves customer 2 => End
- Start
- Scenario 2:
- Start
- -> Waiter takes order from customer 1
- -> takes order from customer 2
- -> serves customer 2
- -> serves customer 1 => End
- Start
시나리오 1이 안되면 customer 2는 매우 오래 기다려야 할 것이므로 불만이 생길 것이다.
Example: In a Restaurant (Scenario 1)
Example: In a Restaurant (Scenario 2)
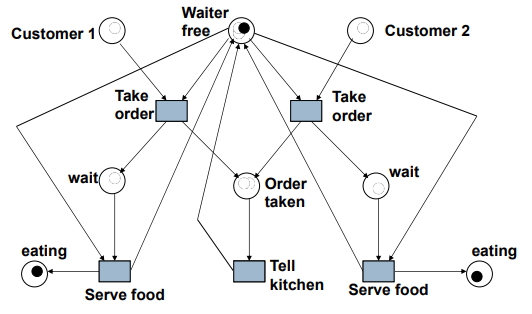
둘 중에 결정하는 transition은 없음
두 개가 한꺼번에 만족 되면 그 중 하나의 transition으로만 이동해야 함.
- 어느쪽으로 갈지는 여기서는 결정 하지 않음
State Charts
- Harel’s state charts are a form of STN, to address problems.
- Hierarchy is used within a single diagram to show alternative and concurrent states.
- Used in UML (Unified Modelling Language)
- Extension to STN
- Example Problem: A television control panel.
- The controller has five buttons “on”, “off”, “mute”, “sel” and “reset”
- The TV is either ON or in STANDBY mode
- When On, user can control the sound with the Mute button and the channel with the Sel Button.
State Charts (A television control panel)
- Extension to STN
- Hierarchy
- Two concurrent sub-nets
- Escapes
- OFF always active
- History
- Link marked H goes back to last state on re-entering subdialogue
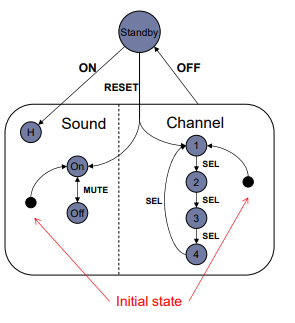
H: history ; 이전 상태
reset 버튼 누르면 default 값( Initial state)으로 간다.
Three Toggles
- Toggles now tidy to represent in State Charts
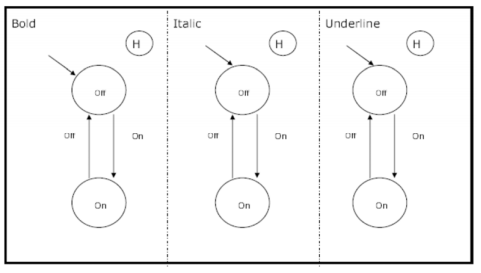
Flowcharts
- Familiar toprogrammers
- Boxes
- Process/Event
- Not state
- Use for dialogue (not internal algorithm)
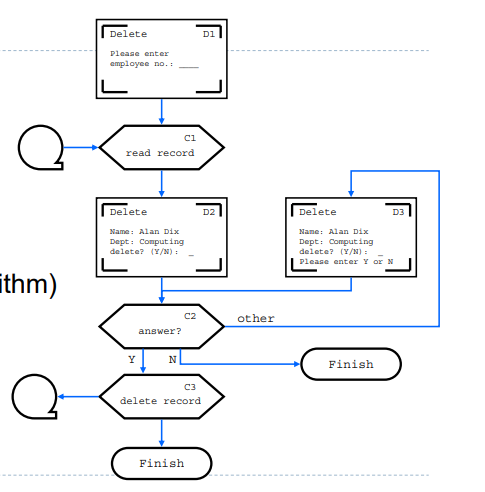
It works!
- Formal notations – too much work?
- COBOL transaction processing
- Event-driven – like web interfaces
- Programs structure ≠ dialogue structure
- 그냥 다음 프로세스가 무엇인지를 알려주는 구조
- Used dialogue flow charts
- Discuss with clients
- Transform to code
- Systematic testing
- 1000% productivity gain
- Formalism saves time!!
JSD Diagrams
- Jackson Structured Design (JSD)
- For tree structured dialogues
- Sequence determined left to right
- Less expressive
- Greater clarity
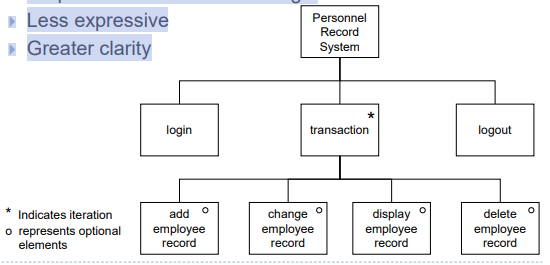
-
*은 iteration 표시
-
동그라미는 option으로 여러 선택지 중 하나를 수행(left에서 right으로 가는 것이 아니라)

댓글남기기